Cancer is a group of diseases
Cancer Treatment In India
• Cancer is a genetic disease:
– Inherited cancer
– Sporadic cancer
• Cancer typically involves a change in gene
expression/function:
– Qualitative change
– Quantitative change
• Any cancer causing genetic alteration typically results in
loss of cell growth control
What is Cancer?
Malignant Vs. Benign growth
• Benign: called a tumor
– Well circumscribed, slow growing, non invasive, non metastatic.
• Malignant: called a cancer
– Not well organized, irregularly shaped, fast growing, infiltrative
growth, metastatic.
• Initial stages of malignant cancer may typically show
benign growth;
– further accumulation of mutations may make it malignant.
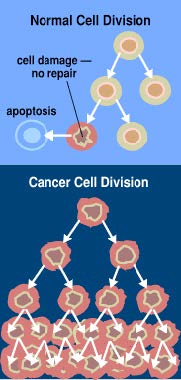
• Cancer arises from a loss of
normal growth control.
• In normal tissues, the rates of
new cell growth and old cell death
are kept in balance.
• In cancer, this balance is
disrupted. This disruption can
result from uncontrolled cell
growth or loss of a cell's ability to
undergo "apoptosis."
• Apoptosis, or "cell suicide," is the
mechanism by which old or
damaged cells normally selfdestruct
Properties of Cancer Cells
• Cancer cells exhibit several characteristics that are distinct from
normal cells.
• Multiple changes are involved in the conversion of a normal cell
to a cancer cell:
– Autocrine stimulation; grow in the absence of growth factors
– Lack of gap junctions;
– lack of contact inhibition
– Resistance to cell death; persistent telomerase activity
– Rapid growth; overtake population, invade other tissues.
– Angiogenesis
– Clonal nature of cancer
– Genomic Instability: Accumulation of successive mutations
• A germline mutation causes a hereditary cancer.
• A somatic mutation causes a sporadic cancer.
Properties of Cancer Cells:
Changes that produce a potential for immortality
• Loss of limitations on the number of cell divisions
• Ability to grow in culture – normal cells do not grow well in culture
• Restoration of telomerase activity
Properties of Cancer Cells:
Changes that enable tumor to disrupt local tissue and invade
distant tissues
Ability to metastasize
• Angiogenesis – secrete substances that cause blood vessels to
grow toward tumor
• Evasion of immune surveillance
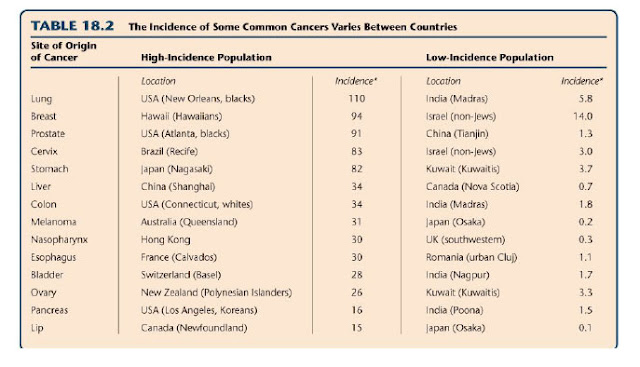
• If one sib or twin gets cancer, other usually does not
Most cancers result from exposures to mutagens
- • Populations that migrate – profile of cancer becomes more like people
- indigenous to new location
Sporadic Vs. Familial Cancer
• Familial:
• inherited form. The family has a predisposition through a
germline mutation.
– Increases the probability that further mutations will occur.
– Sometimes the initial germline mutation may be responsible
for different cancers:
• e.g. same family may have individuals with breast, bone, lung, ovarian
cancer because of a single inherited germline mutation:
• Sporadic cancers:
• new mutations arising in somatic cells of the body.
– Could result in any type of cancer, depending on the where the
mutation occurs.
Inheritance of a mutation in a "cancer protection" gene in a germ
cell (egg or sperm). The offspring will have both a faulty copy and a
correct copy of the "cancer protection" gene in all the cells of their
body, and will be predisposed to develop cancer.
Genes and Cancer
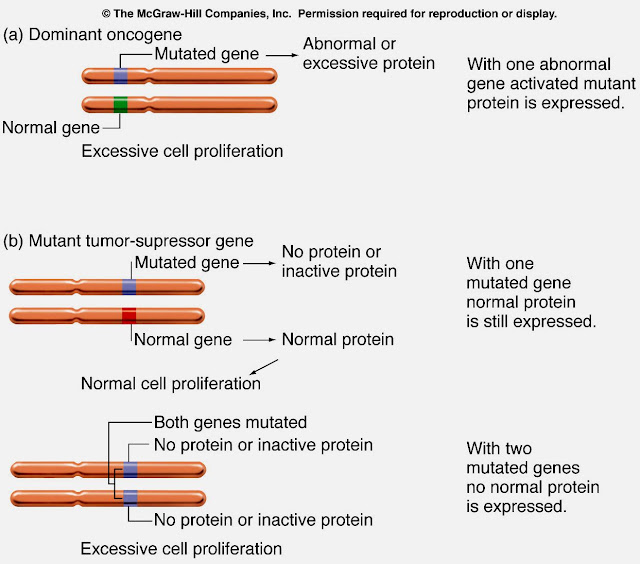
• Two classes of genes are mutated frequently in cancer:
– Tumor suppressor genes: loss of function mutations.
• Normal function is to prevent cell proliferation.
• So-called “cancer protection” genes
– Protooncogenes: gain of function mutations.
• quantitative change in expression of these genes common in cancer
• Normal function is to promote cell proliferation.
Oncogenes
– dominant
mutations
• Mutant tumorsuppressor
genes
– recessive
mutations
Multistep Nature of Cancer
• Cancer develops progressively as mutations accumulate.
• Experimental evidence in mice with either the ras OR the myc
protooncogenes mutated: fewer tumors develop than when BOTH
genes are mutated.
• Mice with only one allele of the tumor suppressor p53 mutated are
not as cancer prone as when both alleles are mutated.
• Hereditary adenomatous polyposis or Familial adenomatous
polyposis (FAP):
– a typical example of the multi-step pathway for cancer.
Multistep Nature of Cancer
The Multi-Step Model
Genomic Approaches to Cancer
Diagnostics and Therapies
• Cancer Diagnostics Goal:
• Properly classify the type of cancer
• To properly treat that specific type
• Usually done by morphology,
• Certain tumor surface markers,
• and Identification of translocations
• Now, genomic approaches can help
• Determine the gene expression array of the tumor
• Compare to tumors with known patient outcome
• Gene profiling
•Example: Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma, DLBCL
Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma, DLBCL

Doctor for Cancer in Delhi. Call Us: +91 9811996326, Email Us: kundan25@gmail.com Know More: http://oncocare.in/


















No comments:
Post a Comment